Your Cart is Empty
Menu

The Ultimate Guide to How Electric Bike Works
April 29, 2024

Electric bikes, with their innovative electric motors, offer an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional transportation. As more people seek sustainable ways to travel, e-bikes are becoming a popular choice. They not only make commuting easier and more enjoyable but also significantly reduce carbon emissions.
Key Takeaways
- E-bikes are made up of an electric motor, a battery, a controller, sensors, and often a display or throttle. These parts work together to provide motorized help, like a pedal assist or a throttle.
- Electric bikes use two main types of motors: mid-drive and hub. Mid-drive motors integrate well with bike gears for a smoother ride on rugged terrains, while hub motors are less expensive and simpler and affect the bike's balance but are easier to maintain.
- E-bikes are divided into three classes based on speed and whether they use pedal assist or throttle. These classes determine where you can legally use e-bikes and what rules apply.
This guide breaks down everything you need to know about electric bikes. It covers the mechanics, the benefits, and what to look for when purchasing your e-bike.
What is an Electric Bike?

Electric bikes have rechargeable batteries that power the motor, which kicks in when you pedal. Some models also have a throttle mode that lets you use the motor without pedaling. You can adjust the level of assistance to suit your needs, from light to strong support.
Electric bikes make cycling easier and more accessible, ideal for daily commutes, leisure rides, or those who need a less physically demanding option due to health reasons or challenging terrains. They offer the environmental advantages of traditional bikes while improving mobility and minimizing effort, making them a practical choice for sustainable travel.
These bikes are fitted with electric components such as a motor, battery, and controller to assist with pedaling. They help you pedal easier, let you go faster, climb hills with less effort, and travel further without getting as tired as you would on a regular bike.
While the concept of assisted bicycles has existed since the late 1800s, recent advancements in battery and motor technology have revolutionized e-bikes. They're now sleeker, lighter, and more accessible than ever, so it's no wonder they're becoming popular for people from all walks of life.
Looking for an eBike that delivers top battery efficiency? Browse B.O.B. Electric Bikes now!
Key Components of an Electric Bike

This should include the main components: motor (mid-drive or hub), battery, controller, sensors, and display/throttle)
Think of your e-bike as a clever combination of classic bicycle parts and some high-tech additions. Understanding the main components will help you make an informed decision as you explore your options.
Motor
The electric motor is what sets your e-bike apart from a standard bicycle. It's the powerhouse responsible for providing extra assistance whenever you need it. There are two main types of motors you'll encounter:
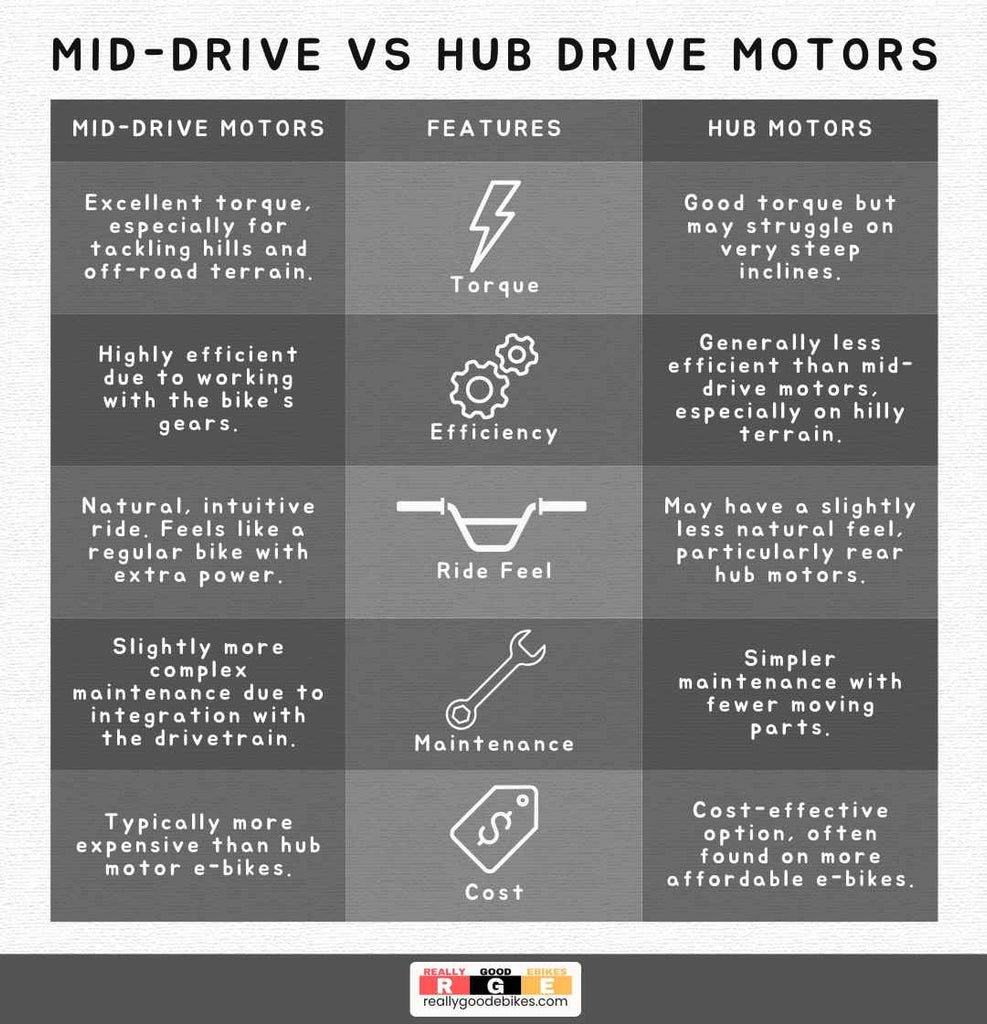
Mid-drive Motors:Located at the center of the bike near the pedals, mid-drive motors are known for their smooth and natural-feeling power delivery. They work in sync with your gears, allowing you to efficiently tackle hills and challenging terrain. While slightly more expensive, mid-drive motors provide the most integrated and intuitive riding experience.
Hub Motors: Found within either the front or rear wheel hub, hub motors offer a different kind of ride. They are robust and easy to maintain, making them an excellent option for budget-conscious riders or those looking for a less complicated setup. Remember that hub motors can sometimes affect the bike's balance, depending on whether they're in the front or rear wheel.
Here's a table outlining the differences between mid-drive vs. hub motors:
Battery
The battery is the heart of your e-bike adventure. It usually consists of multiple lithium-ion cells, similar to those found in laptops or power tools.
When selecting a touring e-bike, carefully considering the battery specifications is essential. The capacity, measured in watt-hours (Wh), determines your range. For instance, a 500Wh battery typically provides a longer range on a single charge than a 300Wh battery. When choosing the capacity, consider the length of your usual commute or ride.
Batteries can be integrated into the bike's frame, mounted on the downtube, or placed on a rear carrier. The placement impacts the bike's look and weight distribution. Batteries integrated into the frame usually appear more streamlined but may be slightly more difficult to remove for charging.
E-bike batteries degrade over time and gradually lose their ability to hold a charge. It's helpful to check the battery's lifespan in terms of "charge cycles," where one cycle is a full charge and discharge. Higher-end batteries can last over 1000 cycles. Importantly, most e-bike batteries are replaceable, allowing you to extend the life of your e-bike even if the original battery's performance declines.
Controller
Think of the controller as the brain of your e-bike's electrical system. This sophisticated technology takes information from the sensors, the battery, and your input to manage how much power the motor receives.
A good controller ensures smooth operation, extends the battery's range, and includes features such as regenerative braking, which slightly recharges the battery while you brake, especially downhill. Advanced controllers may also let you customize e-bike motor support for each assist level to suit your preferences.
Sensors
Sensors provide crucial data that helps your e-bike understand how to assist you best. There are two main types: pedal assist system (PAS) and torque sensor.
- A Pedal Assist System PAS) typically includes a magnet disc attached to your pedal crank and a sensor near the frame. As you pedal, the sensor detects the rotation and signals the motor to engage. PAS systems often have multiple assist levels, letting you choose how much of a boost you want.
- A torque sensor measures the force you apply to the pedals. The harder you push, the more power the motor delivers. Torque sensors provide a natural and intuitive riding experience that feels like an extension of your effort.
Display/Throttle
The display unit on your handlebars is your window into the e-bike's operation. It typically provides information like your current speed, battery level, assist mode, and distance traveled. Some displays offer additional information like estimated range, power output in watts, or even cadence (your pedal revolutions per minute).
Some e-bikes also have a throttle, giving you an alternate way to engage the motor. An type of electric bike throttle can help get a quick start from a standstill, take a short break from pedaling, or navigate a tricky section without having to shift gears.
How Do Electric Bikes Work?
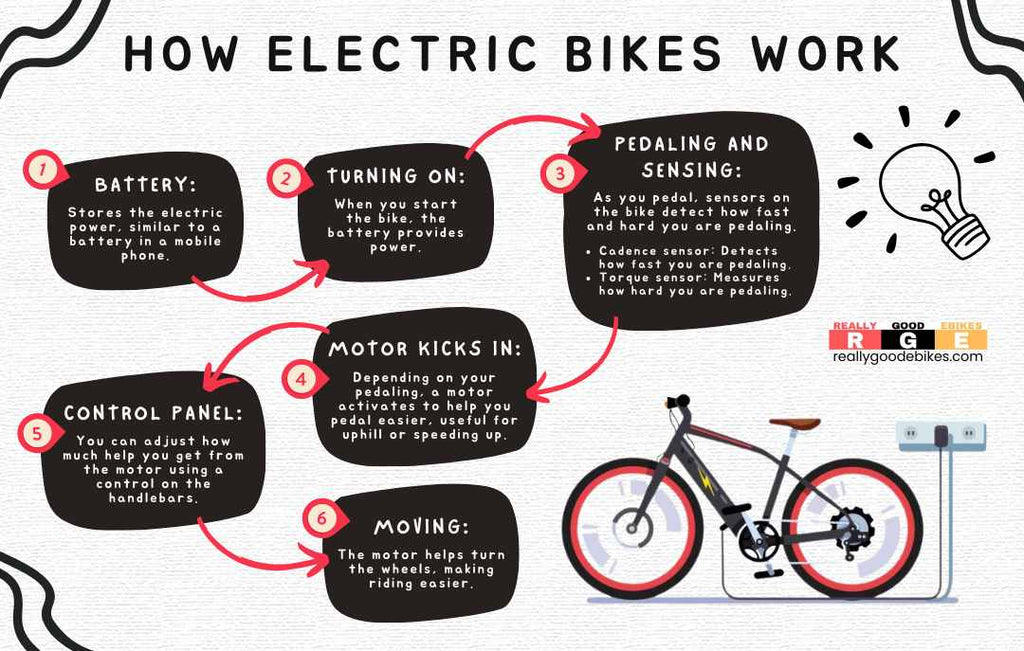
The magic of an e-bike lies in the interaction of its components. Let's break down how the system comes together to give you that boost.
Understanding Pedal-Assist Systems (PAS)
As soon as you start pedaling, a sensor activates. This sensor could be a basic cadence sensor that detects movement or a more advanced torque sensor that measures your effort.
The sensor then sends a signal to the bike’s controller, which acts as the system's brain. The controller analyzes the sensor's signal and your chosen pedal assist setting. It then instructs the motor on how much power to provide. The motor then activates, offering a smooth boost that enhances your pedaling.
Most pedal-assist e-bikes have several assist levels, such as "Eco," "Tour," or "Sport." These settings control the level of boost you receive. The boost is mild in "Eco" mode, while "Sport" mode provides maximum power. These options allow you to customize the assistance based on your fitness level and the type of ride.
Learn how eBikes work, then get your own! Browse Nakto USA Electric Bikes today!
Throttle-Only Systems
Some e-bikes use a throttle system instead of sensors, allowing you to control the motor with a twist of your wrist, whether you're pedaling or not. Throttle-only systems, including a twist grip or a thumb lever on the handlebar, let you directly control the motor's power.
Using a throttle-only e-bike is like riding a scooter and provides a different experience from pedal-assist bikes. You can easily engage the motor anytime, even from a stop, which is handy for quick starts at intersections or climbing steep hills.
It's important to note that throttle-only e-bikes might not be legal for street use everywhere, so you should check the local regulations in your area. Although you won't get as much of a workout compared to pedal-assist bikes, throttle-only e-bikes offer a fun and convenient way to travel.
This video explains the working of electric bikes with 3D animation.
The Different E-Bike Classes
E-bikes are often categorized into classes to help regulate where they can be ridden and who can ride them. While the exact laws vary between states and regions, a common three-class system provides a good framework. Let's break it down.
Class 1: Pedal-Assist Only
Average price range: $1,000 - $3,000
Typical weight limit: 250-300 lbs (rider and cargo combined)
These e-bikes provide assistance up to 20 mph (32 km/h), and the motor stops assisting. They operate solely with a pedal-assist system, meaning the motor kicks in when you start pedaling and disengages when you stop. Class 1 e-bikes generally have the fewest restrictions and are often allowed on most bike paths and trails where traditional bikes are permitted.
Class 2: Throttle and Pedal-Assist
Average price range: $1,500 - $3,500
Typical weight limit 250-300 lbs (rider and cargo combined)
Class 2 e-bikes also offer a power boost of up to 20 mph (32 km/h), but they feature both pedal assist and a throttle. This means you can choose whether to engage the motor by pedaling or by using the twist-grip throttle. Due to the throttle option, Class 2 e-bikes may face certain restrictions on bike paths and multi-use rail trails, so checking your local regulations is essential.
Class 3: Speed Pedelec
Average price range: $2,500 - $5,000+
Typical weight limit: 250-300 lbs (rider and cargo combined)
This class offers the most powerful assistance, allowing you to reach up to 28 mph (45 km/h) while the motor is engaged. They function with pedal assist only. Class 3 e-bikes are often not allowed on standard bike paths due to their higher speeds. Some areas, such as mopeds, might be regulated, which potentially require a license or registration.
The class system is important because it helps ensure the safety and appropriate use of e-bikes on shared paths. Understanding the different classes allows you to choose an e-bike that aligns with your needs and know where you can ride it legally.
Choosing the Right Electric Bike For You
Finding the ideal e-bike is like matchmaking – you want to find the perfect combination of features that suits your lifestyle and riding goals. Here’s a quick overview of the different types of e-bikes:

Now that you know the types, you have to consider the following factors:
Intended use
Think carefully about where and how you'll primarily use your e-bike. If you aim to replace car trips or beat traffic, a commuter is the best e-bike to get.
Look for features like sturdy racks to carry your bag, fenders to keep you clean in rainy weather, and integrated lights for safety. For scenic bike paths, casual weekend rides, or staying active, consider a comfort cruiser-style e-bike with an upright riding position or a hybrid e-bike that blends comfort and efficiency.
Desired range
Consider how far you typically ride or would like to ride with the assistance of an e-bike. For errands around the neighborhood or quick commutes, a smaller, lighter battery will suffice. This can also lower the overall cost of the e-bike. If you plan on touring, extended trail days, or have a lengthy commute, invest in a higher-capacity battery to avoid range anxiety.
Rider fitness level
E-bikes are a game-changer for all fitness levels, but how much of a workout you want plays a role in your choice. Opt for a lighter-weight e-bike with a less powerful motor for more workouts.
Use the lowest assist settings to get your heart pumping while still enjoying the extra push. If you're recovering from an injury, want to easily tackle challenging hills, or simply maximize the ease of riding, a more powerful motor, and multiple assist levels offer great flexibility.
Budget
E-bikes come in a wide range of price points, generally between $1,000 to $5,000. Determine your realistic budget early on. Keep in mind that cheaper ebikes isn't always better! Spending a little more upfront on a quality build can save you money on repairs and replacements in the long run.
Component quality
Just like with traditional bikes, the quality of components makes a difference. Research reputable brands that offer reliable motors and long-lasting batteries. Don't overlook the quality of the brakes, gears, and shifters. These impact the overall riding experience and longevity of your e-bike.
Maintenance and Care for Your E-Bike
Taking good care of your e-bike ensures it lasts for many enjoyable rides. While e-bikes require some of the same maintenance as traditional bicycles, they also have unique needs due to their electrical components.

Cleaning: It's important to keep your e-bike clean. Dirt can reduce the drivetrain's efficiency (like gears and chains). When cleaning, avoid using high-pressure water on electrical parts as it could damage them. Use a damp cloth, mild bike soap, and a soft brush instead. Make sure to keep water away from electrical connections.
Chain Maintenance:A clean and lubricated chain improves the performance of both pedal-assist and throttle modes. Clean the chain with a degreaser and apply a lubricant suitable for your riding conditions. Regularly check the chain for wear and replace it if necessary to protect your gears.
Brakes:Brakes are crucial for safety, especially because e-bikes can reach higher speeds. Regularly check your brake pads for wear and ensure the brake levers feel firm and responsive. Learn how to adjust your brakes or take your bike to a shop for more complicated maintenance.
Tires:Keep your tires properly inflated to the pressure recommended on the tire sidewall. This enhances efficiency, protects the rims, and maximizes the bike's range. Check for and replace worn or damaged tires as needed.
Battery Care: The battery is a vital part of your e-bike. Avoid extreme temperatures and follow the manufacturer's charging instructions. Do not leave the battery fully charged or completely drained for long periods. If you experience battery problems, start by checking connections to ensure everything between the battery and the bike is securely connected and there's no corrosion buildup.
If the problem continues, consult your e-bike's user manual and don't hesitate to contact the manufacturer of your e-bike or the retailer where you purchased it.
The Future of Electric Bikes
Advances in battery technology lead to smaller, lighter batteries offering more energy. As a result, e-bikes can travel longer distances with a sleek design that looks similar to traditional bicycles.
Ebike trends also show increased integration of technology. E-bikes now have better displays, can connect to smartphones for tracking rides, and include advanced features like GPS and anti-theft systems.
Innovation in sensors, especially torque sensors, is also improving. These sensors help the e-bike assist your pedaling in a natural and responsive way.
Research and projections paint an optimistic picture of e-bikes' growth. The European Cyclists Federation predicts that by 2030, there will be 30 million e-bikes sold annually around the world. This underscores their immense potential to transform the way we move.
As more people consider e-bikes as a viable alternative to cars, there's the potential to significantly reduce traffic congestion and pollution. E-bikes offer a sustainable, healthy, and often faster way to navigate urban environments, especially for those who might have previously felt limited by distance or hills.
Ready to Ride? Your E-Bike Journey Starts Here
The beauty of electric bikes lies in their ability to unlock new possibilities. Whether exploring longer routes or feeling the wind in your hair with less effort, e-bikes expand what you thought was possible on two wheels.
With so many different e-bike styles, features, and price points available, choosing the right one can seem daunting. By understanding the basics of e-bikes, the different classes, and your own needs as a rider, you'll be empowered to make an informed decision and find the perfect e-bike to enhance your adventures.

Frequently Asked Questions
Do electric bikes charge as you ride?
Some electric bikes are equipped with regenerative braking, which allows them to recharge slightly while you ride, particularly during braking. However, this feature is not common, and the amount of charge gained is minimal.
Do electric bikes work without power?
Yes, electric bikes can be ridden without power, functioning just like a regular bike. However, they are usually heavier than non-electric bikes due to the added components like the motor and battery.
Do you still have to pedal an electric bike?
Yes, you typically need to pedal an electric bike to activate the motor, except for models with a throttle that can propel the bike without pedaling.
1 Response
Leave a comment
Comments will be approved before showing up.
Also in Really Good Ebikes: Electric Bike Blog
Your are successfully subscribed for email notifications.
Notify me when available
We will send you a notification as soon as this product is available again.
Your email is required
We don't share your email with anybody
x



Gustavo Salas
October 31, 2025
Thanks for this useful information